In the global race to combat climate change, carbon sequestration has emerged as a crucial strategy to reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Among the various methods available, biochar has recently been stealing the spotlight, and for good reason. This carbon – rich material, derived from organic waste, not only offers a way to lock away carbon for centuries but also brings a host of additional environmental and agricultural benefits. A key factor behind the growing success of biochar in carbon sequestration lies in the advancement and widespread use of biochar production equipment.
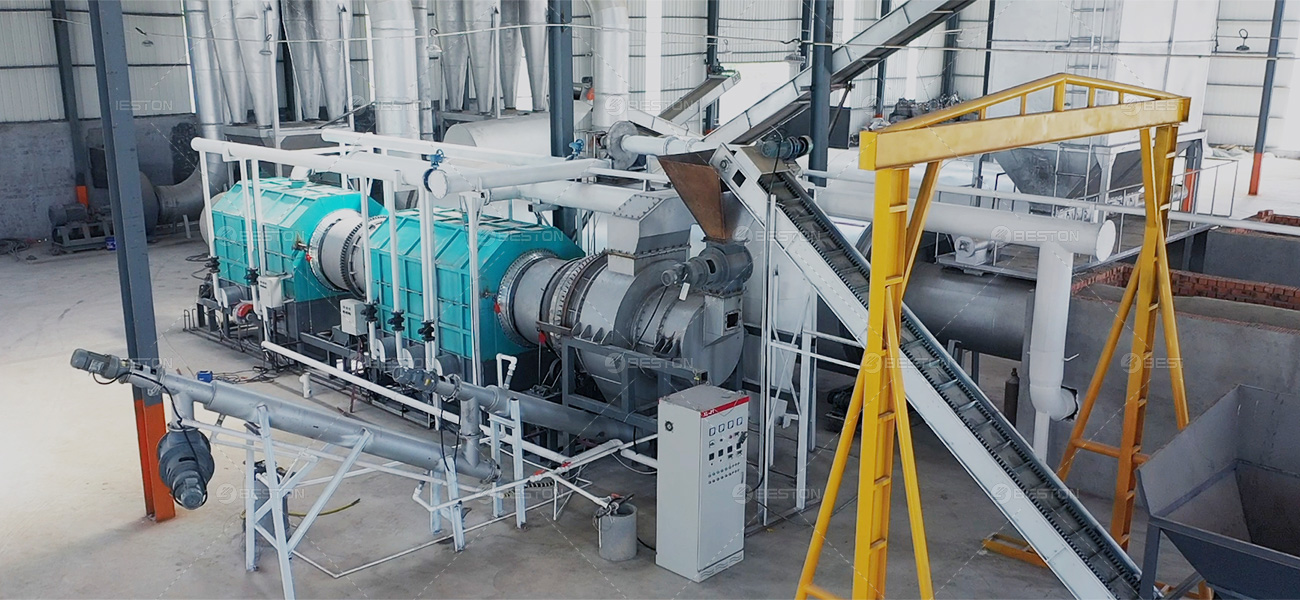
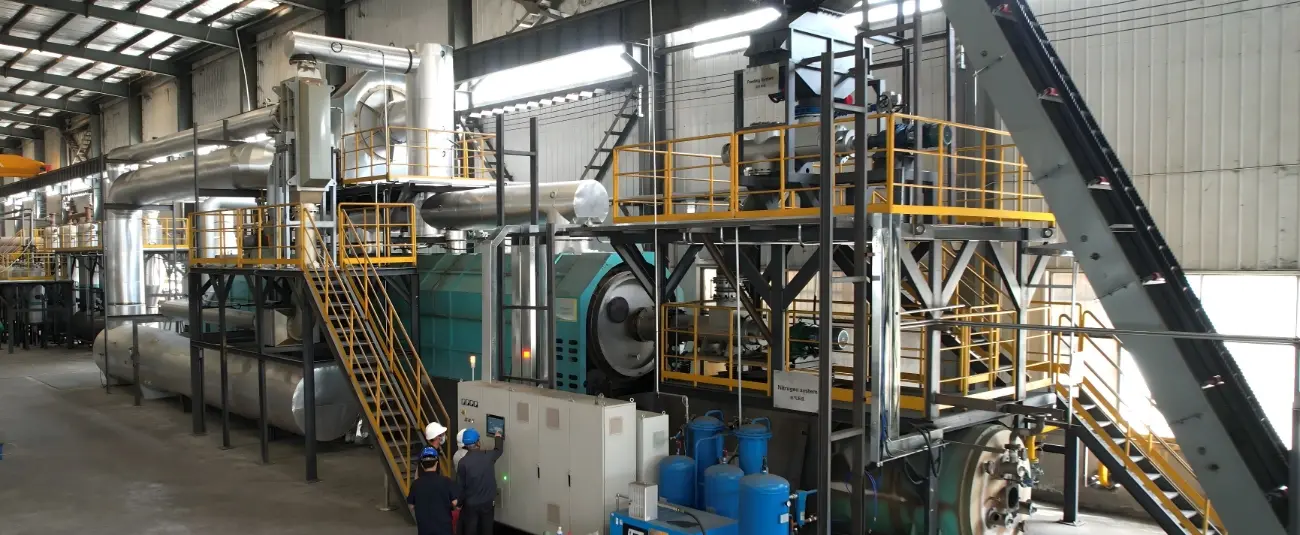
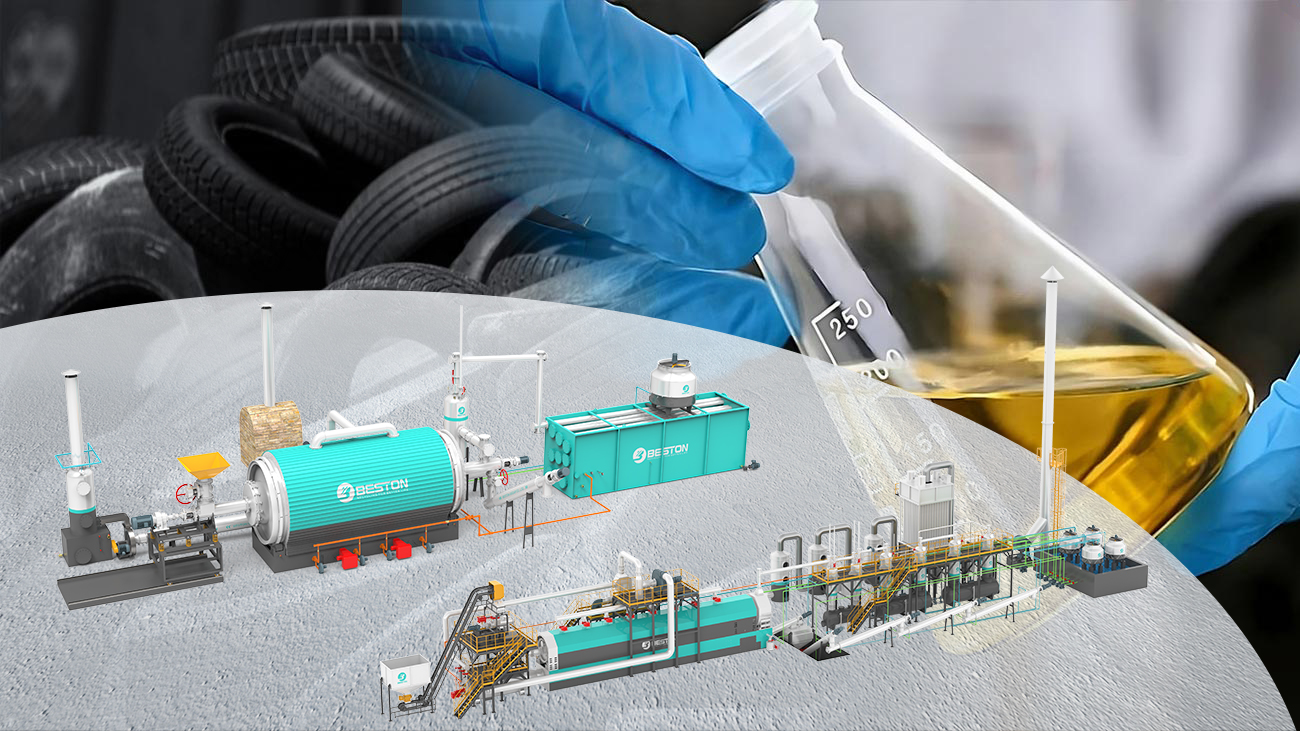
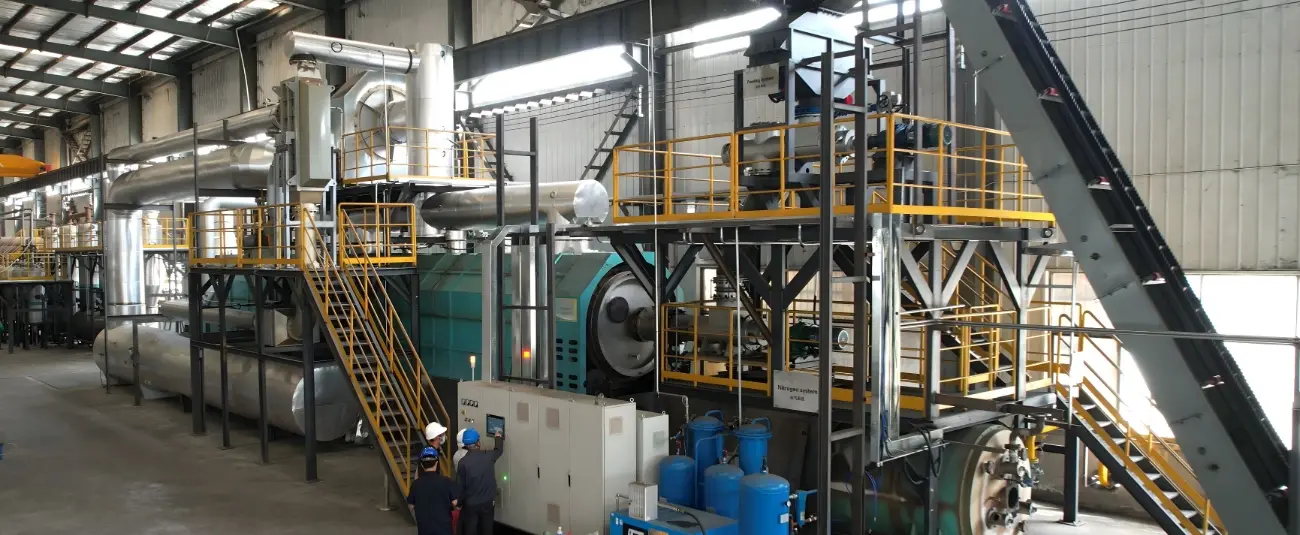
First and foremost, biochar’s exceptional ability to sequester carbon stems from its unique chemical structure. When organic materials such as agricultural residues, forestry waste, or even municipal solid waste undergo pyrolysis – a process of heating in the absence of oxygen – they are transformed into biochar. This process stabilizes the carbon in the organic matter, preventing it from being quickly released back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide through decomposition or combustion. Unlike other organic materials that decompose within a few years, biochar can remain in soil for hundreds to thousands of years, effectively acting as a long – term carbon sink. And it is biochar production equipment that makes this pyrolysis process efficient and scalable. Modern biochar production equipment is designed to control temperature, pressure, and oxygen levels with precision, ensuring that the organic materials are converted into high – quality biochar with maximum carbon content. Whether it is small – scale units used by local farmers or large – scale industrial systems, these equipment pieces play a vital role in producing biochar consistently and in large quantities.
Another reason why biochar excels in carbon sequestration is its positive impact on soil health, which in turn enhances the soil’s own carbon sequestration capacity. When biochar is added to soil, it improves soil structure, increases water retention, and provides a habitat for beneficial microorganisms. These improvements allow plants to grow more vigorously, and as plants photosynthesize, they absorb more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their biomass and the surrounding soil. The production of biochar, facilitated by biochar production equipment, also helps to reduce waste. Instead of letting organic waste rot in landfills, where it releases methane – a potent greenhouse gas – or burning it, which releases carbon dioxide, we can convert it into biochar. This not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also creates a valuable resource that can be used to improve soil quality and sequester carbon. Biochar production equipment comes in various types to accommodate different feedstocks and production needs. For example, some equipment is specifically designed to handle agricultural residues like straw and corn stalks, while others can process wood waste from forests or construction sites. This versatility makes it possible to utilize a wide range of organic waste materials for biochar production, maximizing the potential for carbon sequestration.

Furthermore, the use of biochar in carbon sequestration is a cost – effective and sustainable solution. Compared to other carbon sequestration technologies such as carbon capture and storage (CCS) in power plants, which require significant upfront investment and complex infrastructure, biochar production and application are relatively simple and affordable. Small – scale farmers in developing countries can even use low – cost biochar production equipment to produce biochar from local organic waste, improving their soil fertility and contributing to carbon sequestration at the same time. Additionally, biochar has a range of co – benefits that make it an attractive option. It can reduce the need for chemical fertilizers, as it helps to retain nutrients in the soil, and it can also mitigate soil acidity. These benefits not only support sustainable agriculture but also make the adoption of biochar more appealing to farmers and land managers.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on developing more advanced biochar production equipment to further improve the efficiency and sustainability of biochar production. Researchers and engineers are working on equipment that can capture and utilize the by – products of pyrolysis, such as syngas and bio – oil. Syngas can be used as a fuel to power the biochar production equipment itself, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels, while bio – oil can be refined into transportation fuels or other valuable chemicals. This closed – loop system not only makes biochar production more energy – efficient but also increases its economic viability.
In conclusion, biochar’s ability to sequester carbon for the long term, improve soil health, reduce waste, and its cost – effectiveness and sustainability have made it a star player in the field of carbon sequestration. And biochar production equipment is the backbone of this success, enabling the efficient, scalable, and versatile production of biochar from a wide range of organic materials. As we continue to face the challenges of climate change, investing in the development and deployment of biochar production equipment and promoting the use of biochar will be essential steps towards achieving our carbon reduction goals and building a more sustainable future.